|
|
External Parasites on Swine
External parasites of swine are a serious problem for Florida producers. Arthropod parasites limit production by feeding on blood, skin, and hair. The wounds and skin irritation produced by these parasites result in discomfort and irritation to the animal. In Florida, the major pests on swine are lice, mange mites, ticks and stable flies, although horse flies, deer flies, mosquitoes and wound-infesting maggots may also cause severe problems.
Hog Lice
The hog louse (Figure 1) is the most frequently found external parasite of swine in Florida. Louse populations increase in late October and egg-laying adults can usually be found until June. High louse populations are usually found throughout the winter; however, lice also remain on the animal during the summer months.

Figure 1. Hog louse.
Infested hogs are continually irritated by the nymphs and adults which pierce the skin to blood feed. Mature lice are about 1/4 inch in length and are gray-brown in color. Adults and nymphs attack principally the legs and folds of skin around the neck and ears. Each female louse lays an average of 90 eggs which are glued to the hairs. Within two weeks the eggs hatch into nymphs which mature in 10 to 14 days.
Feeding lice irritate swine and infestations may be indicated by the animal's behavior. The irritation from louse feeding causes animals to rub or scratch vigorously on any convenient object, leading to weight loss. The skin becomes thickened and sometimes it cracks and produces sores. The presence of louse infestations may be determined by examining the folds of skin around the neck and ears and also between the legs and body.
Mange
Mange in swine is caused by mange mites. Two principal types of mange mites are found in Florida. Itch mites (Sarcoptic Mange (Figure 2)) burrow just beneath the skin making slender, winding tunnels from 0.1 to 1 inch long. Fluid discharged at the tunnel opening dries to form nodules. A toxin is also secreted which causes intense irritation and itching. Infested animals rub and scratch constantly producing inflamed areas which may spread over the entire body. Infestations are contagious and treatment of all animals in a herd is essential to prevent transmission.

Figure 2. Itch mange mite.
When mange is suspected, protect yourself from contamination. Mange can be transmitted to humans. After handling infested hogs, wash clothing in hot soapy water and shower thoroughly.
Follicular mites (Demodectic Mange) (Figure 3) are microscopic, cigar-shaped mites that also live in the skin. All life stages are found in the hair follicle. The mite produces nodular lesions which sometimes break, producing holes in the hide. Control is difficult since the mites are located deep in the hide.

Figure 3. Demodectic mange mite.
Excessive scratching and rubbing may be an indication of mange. Follicular mange may produce inflamed areas and pustules on the belly, the head and top of the neck. To make a positive identification of mange, scrape the edge or margin of suspected areas with a dull knife until bleeding starts or scrape contents of pustules. Examine scrapings under magnification.
Ticks
Several species of ticks may attack swine. These fall under two general groups, hard and soft ticks. Hard ticks are the most important group to attack swine. Hard ticks have a long association with the host, feed slowly, take a large blood meal, drop from the host to molt, and lay many eggs. Typical representatives are the American dog tick (Figure 4), brown dog tick, Gulf Coast tick (Figure 5), and rocky mountain wood tick. Soft ticks (Figure 6) are of less importance to hogs. Soft ticks feed rapidly while a host animal is resting and then leave. A typical soft tick is the spinose ear tick.
|
 |
 |
Figure 4.American dog tick. |
Figure 5.Gulf Coast tick |
Figure 6.Soft tick, O.turicata. |
The effects of ticks on swine are inflammation, itching and swelling at the bite site. Wounds may become infected. Ticks are typically a problem on hogs that are allowed to roam in wooded areas.
Stable Flies
The stable fly (Figure 7) is similar to the house fly in size and color, but the bayonet-like mouthparts for sucking blood differentiate it. Stable fly bites cause irritation to animals and may account for much blood loss in severe cases. Wounds from bites may become infected. Stable flies are proven vectors of swine diseases such as hog cholera and leptospirosis.
Stable flies breed in soggy hay, grain or feed, piles of moist fermenting weeds, spilled green chop, peanut litter, and in manure mixed with hay or straw. Stable fly control is most successfully approached by cultural control measures. The larvae require a moist breeding media. Therefore, the source of breeding should be dispersed to allow drying often enough to break the life cycle.

Figure 8. Stable fly.
Sticktight Flea
The sticktight flea (Figure 9) is an important pest of swine in Florida. Although the flea is mainly considered to be a pest of poultry, the ears of hogs may often become lined with them.
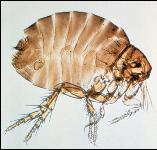
Figure 9. Sticktight flea.
Adult fleas line the ears of swine where they feed on blood and remain attached for several weeks. While feeding, the female lays eggs which fall to the ground. The eggs hatch and the larvae feed on organic matter in dry protected places. Within one month the larvae pupate and transform to adults. Adult fleas feeding in the ears may cause ulceration and secondary infection.
Keys to Pesticide Safety
- Before using any pesticide, stop and read the precautions.
- Read the level on each pesticide container before each use. Heed all warnings and precautions.
- Store all pesticides in their original containers away from food or feed.
- Keep pesticides out of the reach of children, pets and livestock.
- Apply pesticides only as directed.
- Dispose of empty containers promptly and safely
The use of trade names in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information. It is not a guarantee or warranty of the products named and does not signify that they are approved to the exclusion of others.
To avoid excessive residues, use the insecticides recommended at the time recommended and in the amounts recommended. These recommendations are for guidelines only. The user must insure that the pesticide is applied in strict compliance with label directions. The improper use of insecticides may result in residues in meat or fat.
Tables
Table 1.Summary of Swine Insecticide Registrations.
Insecticide
(active ingredient) |
Formulation |
% Active
Ingredient |
Signal
Word |
Pests |
Coumaphos
(Co-Ral Emulsifiable Livestock Insecticide) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
11.6% |
Danger |
lice (Reg 06/2005) |
(Co-Ral Fly and Tick Spray) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
6.15% |
Warning |
lice (Reg 06/2005) |
Permethrin
(Atroban 11% EC Insecticide) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
11.0% |
|
lice, mange (Reg 06/30/2007) |
(Atroban 42.5% EC) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
42.5% |
Danger |
lice, mange (Reg 06/30/2007) |
(Catron IV) |
Aerosol |
0.5% |
Caution |
deer flies, ear ticks, horn flies, horse flies, house flies, gnats, lice, stable flies (Reg 06/30/2007) |
(GardStar 40% EC) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
40.0% |
Danger |
lice, mange (Reg 03/31/2006) |
(Permectrin II) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
10.0% |
Caution |
blow flies, fleas, hog lice, mange mites, mosquitoes, ticks
(Reg 06/2007) |
(SwineGuard) |
Pour-On |
10.0% |
Warning |
lice, mange mites (Reg 03/2006) |
Phosmet
(Del-Phos Emulsifiable Liquid) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
11.6% |
|
lice, sarcoptic mange (Reg - Disc 06/2007) |
(Prolate/Lintox-HD) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
11.75% |
Danger |
lice, sarcoptic mange (Reg 12/2005) |
Tetrachlorvinphos
(Rabon 7.76 Oral Larvacide Premix) |
Feed Additive |
7.76% |
Caution |
house flies (Reg 03/2007) |
Table 2.Registered Insecticides for Specific Swine Pests.
Insectcide
(active ingredient) |
Formulation |
Re-Treatment
Interval |
Pre-Slaughter Interval |
Comments |
Blow Flies |
Permectrin II
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Spray or dip animals. May be applied as a premise spray in barns or animal housing. (Reg 06/2007) |
Deer Flies |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
Fleas |
Permectrin II
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Spray or dip animals. May be applied as a premise spray in barns or animal housing. (Reg 06/2007) |
Gnats |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
Horn Flies |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
Horse Flies |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
House Flies |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
Rabon 7.76 Oral Larvicide Premix(tetrachlorvinphos) |
Feed Additive |
|
|
Prepare feed according to label directions. (Reg 03/2007) |
Lice |
Atroban 11% EC Insecticide (permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Dilute according to label directions. Thoroughly wet animals, including ears. (Reg 06/2007) |
Atroban 42.5% EC (permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
5 days |
Apply as a spray according to label directions. (Reg 06/2007) |
Catron IV
(permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. For blood sucking lice apply to infested area using a stiff brush. (Reg 06/2007) |
Co-Ral Emulsifiable Livestock Insecticide (coumaphos) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
Repeat as necessary |
|
Apply specified diluted dosage for a complete wetting to run-off.
(Reg 06/2005) |
Co-Ral Fly and Tick Spray
(coumaphos) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
Not less than 10 days |
|
Apply specified dosage for a complete wetting to runoff. Treat no more than six times per year. (Reg 06/2005) |
Del-Phos Emulsifiable Liquid (phosmet) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
1 day |
Do not treat sick, convalescent, or stressed animals. Do not apply directly to suckling pigs. (Reg 06/2007) |
GardStar 40% EC
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
|
Dilute according to label directions. Thoroughly wet or dip animals including ears. (Reg 03/2006) |
Prolate/Lintox-HD
(phosmet) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
1 day |
Do not apply directly to suckling pigs. Do not use this product on animals simultaneously or within a few days before or after treatment with or exposure to cholinesterase inhibiting drugs, pesticidesor chemicals. Do not treat sick, convalescent, stressed animals. (Reg 12/2005) |
SwineGuard
(permethrin) |
Pour-On |
2 weeks |
5 days |
Apply as a pour-on according to label directions. (Reg 03/2006) |
Lice (Hog) |
Permectrin II
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Spray or dip animals. (Reg 06/2007) |
Mange Mites |
Atroban 11% EC Insecticide (permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Dilute according to label directions. Thoroughly wet animals, including ears. Repeat in 14 days. (Reg 06/2007) |
Atroban 42.5% EC (permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
5 days |
Apply as a spray according to label directions. (Reg 06/2007) |
GardStar 40% EC
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
|
Dilute according to label directions. Thoroughly wet or dip animals including ears.(Reg 03/2006) |
Permectrin II
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Spray or dip animals. (Reg 06/2007) |
SwineGuard
(permethrin) |
Pour-On |
2 weeks |
5 days |
Apply as a pour-on according to label directions. (Reg 03/2006) |
Mites (Sarcoptic) |
Del-Phos Emulsifiable Liquid (phosmet) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
1 day |
Do not treat sick, convalexcent, or stressed animals. Do not apply directly to suckling pigs.(Reg 06/2007) |
Prolate/Lintox-HD
(phosmet) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
14 days |
1 day |
Do not apply directly to suckling pigs. Do not use this product on animals simultaneously or within a few days before or after treatment with or exposure to cholinesterase inhibiting drugs, pesticidesor chemicals. Do not treat sick, convalescent, stressed animals. (Reg 12/2005) |
Mosquitoes |
Permectrin II
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Spray or dip animals.(Reg 06/2007) |
Stable Flies |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
Ticks |
Permectrin II
(permethrin) |
Emulsifiable Concentrate |
2 weeks |
|
Spray or dip animals.(Reg 06/2007) |
Ticks (Ear) |
Catron IV (permethrin) |
Aerosol |
|
5 days |
Spray on both sides being careful to spray back, withers and forelegs thoroughly. (Reg 06/2007) |
( Source: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/document_ig138 )
| |








